Research on the Stability of Oasis
(2023-2024) How to evaluate, identify and enhance the oasis stability?
Introduction
Oasis regions, with high population and wealth density, their stability and sustainability are crucial for human habitation and ecological balance. This study takes Wensu County in Xinjiang as a case to assess oasis stability using the PPSD (Promotion-Pressure-Support-Destruction) model and provides planning recommendations for sustainable development. It quantifies the promotional effects of human actions on oases, such as water infrastructure and transportation development, as well as pressures like resource consumption and development intensity, along with natural support like water, land, and biodiversity, and destructive forces like disasters and climate.
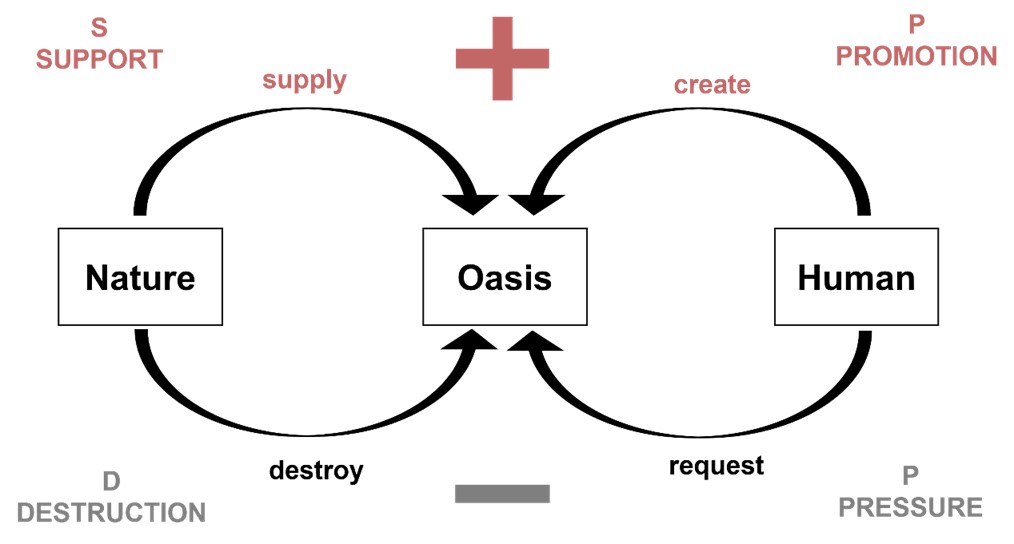
Key Findings
The study reveals that the peripheral areas of Wensu County’s oasis have relatively high stability scores, particularly in the northwest of the western oasis and the south, east, and north of the eastern oasis.
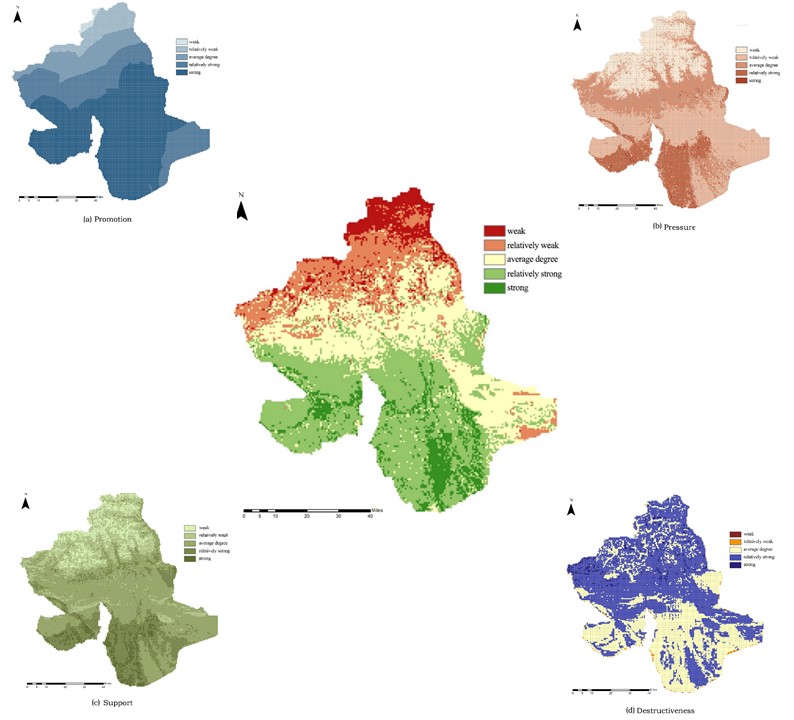
By analyzing the spatial distribution of the four forces, the county is divided into eight ecological zones, with planning and conservation recommendations proposed for each. The study provides scientific support for the sustainable development of Wensu County’s oasis, suggesting a strategy of optimizing the west, controlling the north, stabilizing the east, and connecting the south for spatial planning, land use, and ecological protection and restoration
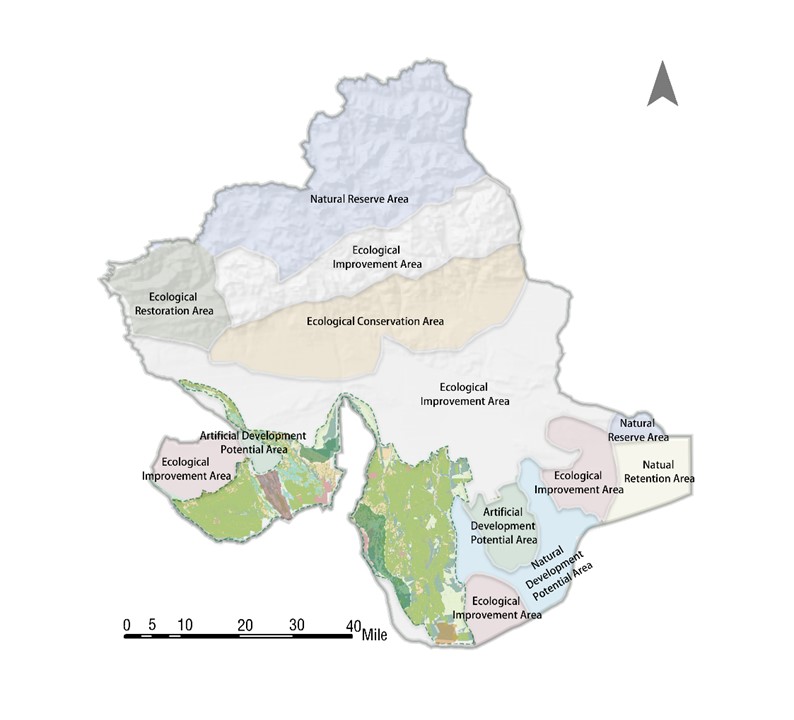
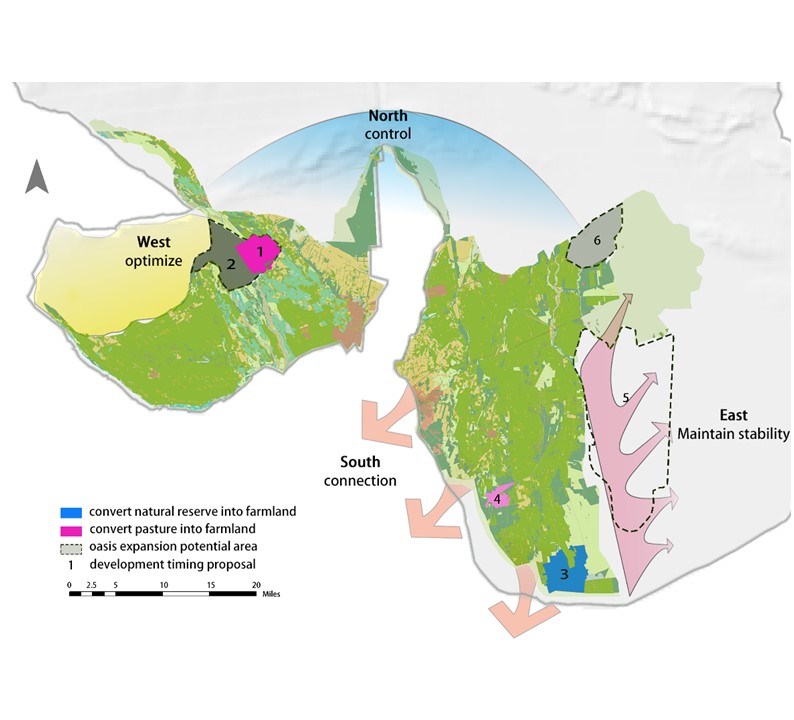
Research Progress
The study has been compiled into a paper titled “Evaluation and Planning Application of Oasis Habitat Stability in Arid Regions Based on the PPSD Model: A Case Study of Wensu County, Xinjiang.”, which was presented orally at the 2024 International Association for China Planning and has been submitted to Journal of Arid Land.